Explain the Concept of Cloud Computing and Its Advantages
Concept of Cloud Computing has undoubtedly reshaped the technological landscape, offering a plethora of that extend across industries.
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, businesses and individuals alike are constantly seeking innovative ways to enhance their efficiency, flexibility, and scalability. One such game-changing innovation that has reshaped the way we store, access, and manage data and applications is cloud computing. In this blog post, we'll delve deep into the concept of cloud computing and explore its numerous advantages that have made it a cornerstone of modern technology.
Understanding the Concept of Cloud Computing
At its core, cloud computing refers to the delivery of various computing services, including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and more, over the internet ("the cloud"). This means that instead of hosting applications and data on local servers or personal computers, users can now access them remotely through the internet from cloud service providers. These services are typically offered on a pay-as-you-go basis, enabling users to scale their resources up or down as needed.
Key Components for Concept of Cloud Computing
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): This foundational layer provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. Users can rent virtual machines, storage, and networking components, allowing for greater flexibility and cost savings.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS offers a platform that includes both the infrastructure and tools needed to develop, deploy, and manage applications. It eliminates the need for managing underlying infrastructure, focusing on streamlining the application development process.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): With SaaS, users access software applications hosted in the cloud. They don't need to worry about installation, maintenance, or infrastructure management. Popular examples of SaaS include Gmail, Microsoft 365, and Salesforce.
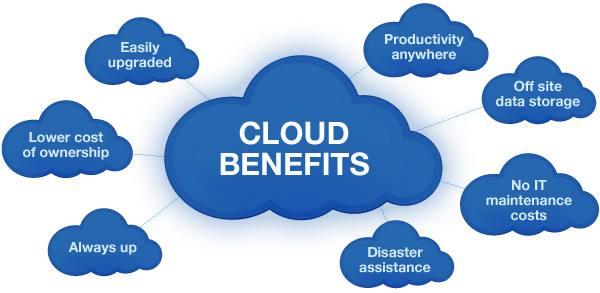
Advantages the Concept of Cloud Computing
Now that we have a basic understanding of cloud computing, let's dive into its myriad advantages:
1. Cost-Efficiency
Traditional IT infrastructure often requires substantial upfront investments in hardware and software. In contrast, cloud computing follows a pay-as-you-go model, allowing users to pay only for the resources they consume. This significantly reduces capital expenses and operational costs, making it an attractive option for both startups and established enterprises.
2. Scalability
One of the most remarkable features of cloud computing is its scalability. Organizations can easily adjust their computing resources to meet changing demands. Whether you need to scale up during a traffic spike or scale down during quieter periods, cloud providers offer the flexibility to do so with minimal effort.
3. Accessibility
Cloud computing enables remote access to data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection. This accessibility is a game-changer for businesses with remote or distributed teams, as it facilitates collaboration and productivity regardless of location.
4. Reliability and Redundancy
Cloud providers typically offer high levels of redundancy and data replication across multiple data centers. This ensures data integrity and minimizes the risk of downtime due to hardware failures or disasters. Many cloud providers guarantee uptime through Service Level Agreements (SLAs).
5. Security
Cloud providers invest heavily in security measures to protect data and applications. They employ dedicated teams of experts to monitor and respond to security threats, making it challenging for individual organizations to match the same level of security in-house.
6. Disaster Recovery
Cloud computing simplifies disaster recovery planning by offering built-in backup and recovery solutions. Data is often stored redundantly across geographically dispersed data centers, ensuring that even in the event of a catastrophic failure, data remains accessible.
7. Automatic Updates
Cloud providers handle software updates and maintenance, ensuring that users always have access to the latest features and security patches without the hassle of manual updates.
8. Environmental Benefits
By sharing resources among multiple users, cloud computing providers can achieve higher energy efficiency and reduce their carbon footprint compared to individual organizations maintaining their data centers. This contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to computing.
9. Global Reach
Cloud computing providers have data centers strategically located around the world. This global reach enables businesses to expand their operations internationally with ease, delivering content and services to a global audience while maintaining low latency.
10. Competitive Advantage
Adopting cloud computing can provide a significant competitive advantage by allowing organizations to innovate faster, reduce time-to-market for products and services, and stay agile in a constantly changing business landscape.
Use Cases of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is not a one-size-fits-all solution; its versatility allows it to cater to various use cases across different industries:
- Business Applications: Organizations can host enterprise-level applications, such as Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, in the cloud for enhanced efficiency and accessibility.
- Data Analytics: Cloud computing offers scalable computing power for processing and analyzing vast amounts of data, enabling data-driven decision-making.
- Web Hosting: Hosting websites and web applications in the cloud ensures high availability and scalability, crucial for businesses with fluctuating web traffic.
- E-commerce: E-commerce platforms leverage cloud computing to handle sales, inventory management, and secure payment processing during peak shopping seasons.
- Development and Testing: Developers use cloud resources for testing and development environments, reducing the need for on-premises infrastructure.
- IoT (Internet of Things): IoT devices generate massive amounts of data, which can be efficiently managed and processed in the cloud.
- Content Delivery: Cloud-based Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) ensure fast and reliable content distribution, improving user experiences for websites and applications.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Cloud providers offer AI and ML services, making it easier for businesses to integrate these technologies into their applications and workflows.
Cloud computing has transformed the way individuals and organizations approach computing, offering a wide range of advantages that cater to diverse needs and industries. Its cost-efficiency, scalability, accessibility, and robust security measures have made it an indispensable tool in the modern digital landscape.
However, it's crucial to note that while cloud computing brings numerous benefits, it also poses certain challenges, including data privacy concerns, vendor lock-in, and potential security vulnerabilities.
Therefore, organizations must carefully evaluate their requirements and choose the right cloud service model (IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS) and deployment model (public, private, or hybrid) to best suit their specific needs.
As technology continues to advance, cloud computing will likely play an even more significant role in shaping the future of business and personal computing. Embracing the cloud can empower organizations to remain competitive, agile, and innovative in a rapidly evolving digital world.
What's Your Reaction?